Abstract
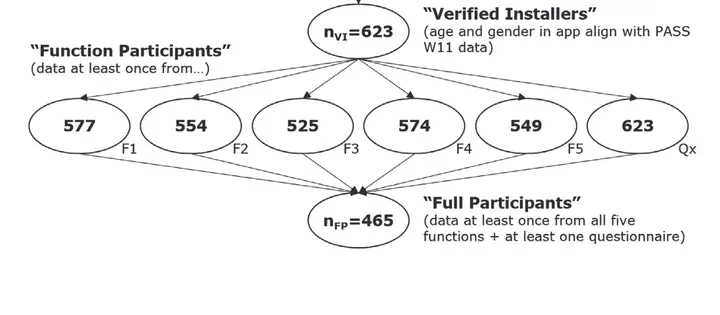
Research apps allow to administer survey questions and passively collect smartphone data, thus providing rich information on individual and social behaviours. Agreeing to this novel form of data collection requires multiple consent steps, and little is known about the effect of non-participation. We invited 4,293 Android smartphone owners from the German Panel Study Labour Market and Social Security (PASS) to download the IAB-SMART app. The app collected data over six months through (a) short in-app surveys and (b) five passive mobile data collection functions. The rich information on PASS members from previous survey waves allows us to compare participants and non-participants in the IAB-SMART study at the individual stages of the participation process and across the different types of data collected. We find that 14.5 percent of the invited smartphone users installed the app, between 12.2 and 13.4 percent provided the different types of passively collected data, and 10.8 percent provided all types of data at least once. Likelihood to participate was smaller among women, decreased with age and increased with educational attainment, German citizenship, and PASS tenure. We find non-participation bias in substantive variables, including overestimation of social media usage and social network size and underestimation of non-working status.